How to size a VFD to motor?
VFDs are current rated devices that are sized based on the amount of current they can provide to the motor. VFD's are typically listed with horsepower (HP) and current rating (Ampres) for both their normal and heavy duty load profile. It is therefore important to confirm the loal profile of the intended application to correctly size a drive.
The load profile is essentially the starting power required to overcome the static inertia. A fan is an example of low overload, when the fan starts, it has low air resitance but as the fan increases in speed the resistant increases and the load does too. A full displacement pump is a good example of a heavy duty load application as the motor pump must overcome the full displament from a cold start.
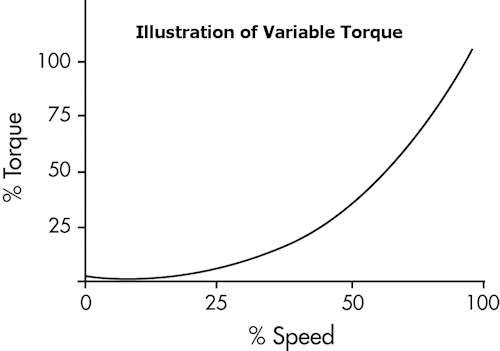 |
Low OverloadDuty rating for applications in which the torque requirements drop along with the speed, such as centrifugal fans, pumps and blower. These loads are typically easier to start (low starting current) and the torque requirements increase substantially with an increase in motor speed. The typical horsepower ratings displayed for the SAI Drive Solutions packaged VFDs are shown as Low Overload, Variable Torque. As the majority of VFD motor loads used in industry are variable torque loads SAI typically quotes HP sizes based on low overload profiles. These HP ratings can be found under the “low overload” rating of the drive. If a High Overload load profile is required then the selection of the device shall be found under the “high overload” rating. SAI will not be held responsible for improper drive selection. |
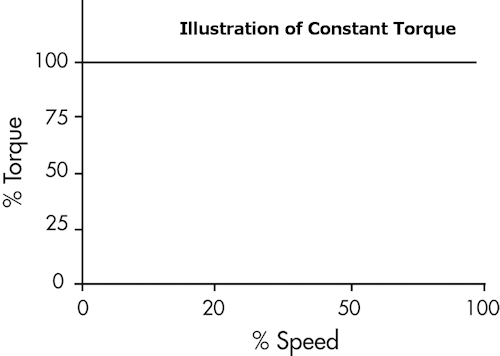
High OverloadDuty rating for applications in which the torque requirements are constant throughout the speed range and include such loads as conveyers, extruders, mixers and full displacement pumps and compressors. These loads are typically harder to start thus with a higher starting current. The current and torque will remain high throughout the motor speed range. |
 |

